Navigating Asbestos Material Risk Assessments vs. Priority Risk Assessments: What You Need to Know as a Duty Holder
As a duty holder, it is your legal obligation to ensure that AMRAs and PRAs are conducted where necessary and that any risks identified are managed effectively

Asbestos is a hazardous material that was widely used in the construction industry until November 1999. It is now known to cause several diseases, including mesothelioma, lung cancer, and asbestosis. As a result, there are strict regulations in place to manage the risks associated with asbestos-containing materials (ACMs). Duty holders, such as building owners, employers, and managers, have a legal obligation to ensure that any asbestos on their premises is managed safely, including conducting asbestos material risk assessments (AMRAs) and priority risk assessments (PRAs).
In this article, I will discuss the differences between AMRAs and PRAs, the legal requirements for both, and provide tips for successful assessments.
Understanding Asbestos Material Risk Assessments (AMRAs)
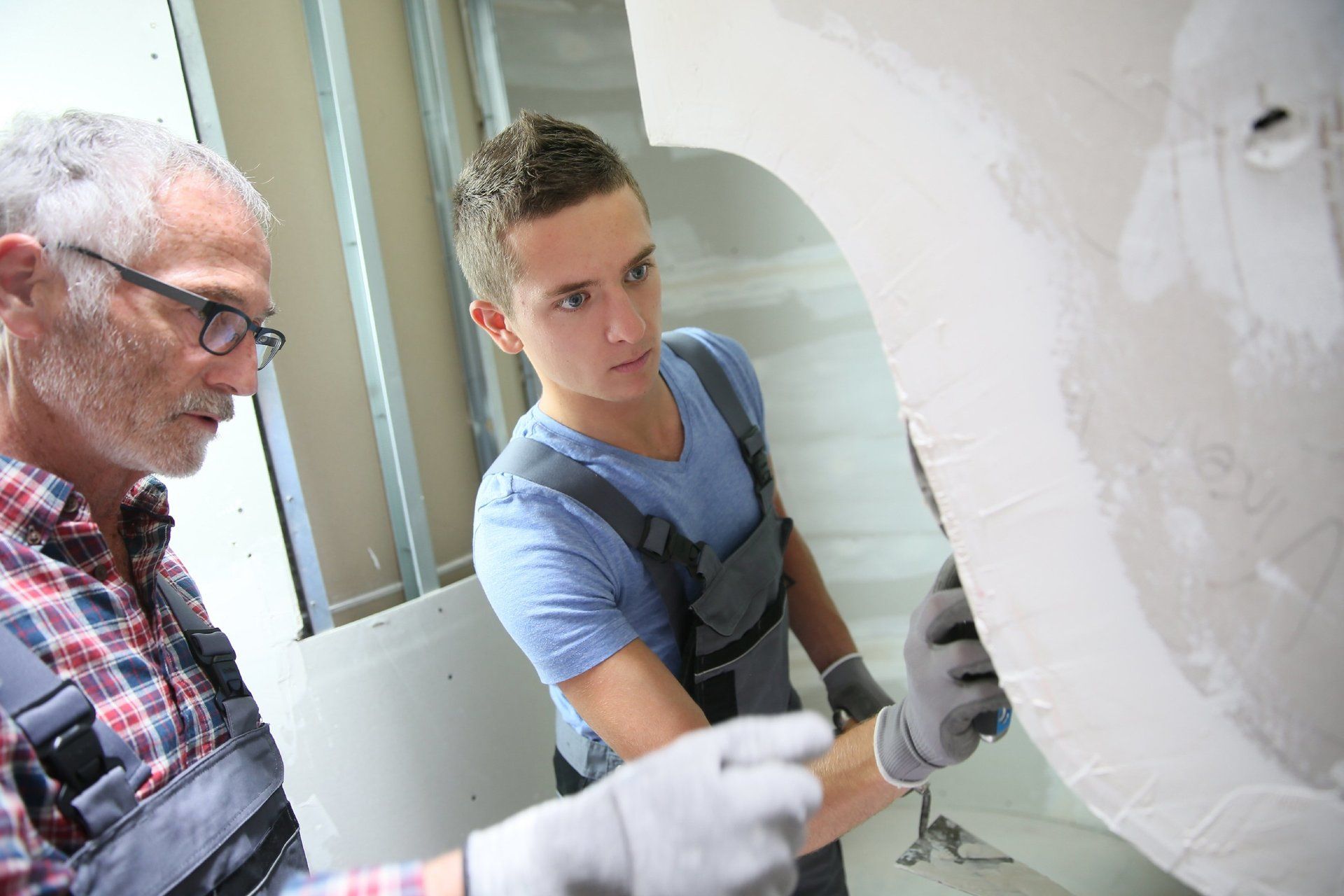
An asbestos material risk assessment (AMRA) is undertaken as part of a detailed survey of a building to identify the presence, location, and condition of ACMs. AMRAs are essential for ensuring the safety of anyone who may come into contact with asbestos-containing materials. The survey should include a visual inspection of the building, followed by sampling and analysis of any suspected ACMs. The results of the AMRA will determine the level of risk posed by the ACMs and inform the development of a plan for managing the risks.
There are three types of survey that will provide you with AMRAs: asbestos management surveys, asbestos refurbishment surveys and asbestos demolition surveys. Management surveys are used to identify the presence, location, and condition of ACMs that may be disturbed during normal occupancy of a building. Refurbishment/demolition surveys are more intrusive and are required when a building is being refurbished or demolished. The survey will identify any ACMs that need to be removed or sealed before the work can proceed.
What is a Priority Risk Assessment (PRA)?
A priority risk assessment (PRA) is a risk assessment that is conducted after an AMRA. The purpose of the PRA is to assess the level of risk posed by the identified ACMs and to determine the priority for managing those risks. The PRA will consider factors such as the location and condition of the ACM, the likelihood of disturbance, and the potential for exposure. The assessment will determine whether the ACM presents a high, medium, or low risk and inform the development of a plan for managing the risks.
Differences between AMRAs and PRAs
The main difference between AMRAs and PRAs is their focus. AMRAs are concerned with identifying the presence, location, and condition of ACMs, while PRAs are concerned with assessing the level of risk posed by those ACMs. AMRAs are a prerequisite for PRAs, as the results of the AMRA will inform the PRA.
Another difference is the level of detail. AMRAs are typically more detailed than PRAs, as they involve sampling and analysis of any suspected ACMs. PRAs may use the results of the AMRA to determine the level of risk, but they do not involve further sampling or analysis.
Legal requirements for AMRAs and PRAs
The Control of Asbestos Regulations 2012 places a legal obligation on duty holders to manage the risks associated with ACMs. This includes conducting AMRAs and PRAs where necessary. The regulations require that AMRAs are conducted on all non-domestic buildings constructed before 2000, and on the common areas of domestic buildings, such as communal stairwells and corridors. Refurbishment/demolition surveys are required before any refurbishment or demolition work is carried out.
PRAs are required following an AMRA to assess the level of risk posed by the identified ACMs. The duty holder must then develop a plan for managing the risks and ensure that this plan is reviewed and updated regularly.
Who is responsible for conducting AMRAs and PRAs?
The duty holder is responsible for ensuring that AMRAs and PRAs are conducted by a competent person. A competent person is someone who has sufficient training, knowledge, and experience to carry out the assessment. The duty holder must also ensure that the assessor has access to all areas of the building and any relevant information, such as building plans, occupancy information and maintenance records.
How often should AMRAs and PRAs be conducted?
The frequency of AMRAs and PRAs will depend on the nature and condition of the ACMs. Management surveys should be reviewed regularly to ensure that the information remains up to date. Refurbishment/demolition surveys should be conducted before any refurbishment or demolition work is carried out.
PRAs should be conducted following an AMRA to assess the level of risk posed by the identified ACMs. The plan for managing the risks should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains effective.
Importance of accurate asbestos identification in AMRAs and PRAs
Accurate identification of ACMs is essential for effective risk management. Failure to identify all ACMs could result in inadequate measures being taken to manage the risks. Similarly, misidentification of non-ACMs as ACMs could result in unnecessary costs and disruption.
The surveyor conducting the AMRA should have sufficient knowledge and experience to identify all types of ACMs. They should also be aware of the common materials that may be mistaken for ACMs, such as textured coatings and certain types of insulation.
Common challenges in conducting AMRAs and PRAs
One of the main challenges in conducting AMRAs and PRAs is gaining access to all areas of the building. This can be particularly challenging in occupied buildings, where tenants may be reluctant to allow access to their premises.
Another challenge is the identification of ACMs in difficult to access areas, such as behind walls and ceilings. The surveyor may need to use specialist equipment, such as borescopes and endoscopes, to access these areas.
Tips for successful AMRAs and PRAs
1. Ensure that the assessor is competent and has sufficient knowledge and experience to carry out the assessment.
2. Provide the assessor with access to all areas of the building and any relevant information, such as building plans and maintenance records.
3. Use specialist equipment, such as borescopes and endoscopes, to access difficult to reach areas.
4. Review the AMRA regularly to ensure that the information remains up to date.
5. Develop a plan for managing the risks identified in the PRA and ensure that it is reviewed and updated regularly.
Conclusion and the importance of prioritising health and safety
Managing the risks associated with ACMs is essential for protecting the health and safety of anyone who may come into contact with them. As a duty holder, it is your legal obligation to ensure that AMRAs and PRAs are conducted where necessary and that any risks identified are managed effectively.
By following the tips provided in this article and working with a competent assessor, you can ensure that your AMRAs and PRAs are successful and that the risks associated with ACMs are managed effectively. Remember, prioritising health and safety should always be your top priority.
If you require assistance with conducting an AMRA or PRA, contact us today to speak with one of our super friendly experienced consultants.